Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D, Neuen BL, Perkovic V. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2021;398:786–802.
Google Scholar
Xie Y, Bowe B, Mokdad AH, Xian H, Yan Y, Li T, et al. Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease study highlights the global, regional, and national trends of chronic kidney disease epidemiology from 1990 to 2016. Kidney Int. 2018;94:567–81.
Google Scholar
G.B.D.C.K.D. Collaboration. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395:709–33.
Google Scholar
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P. Chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 2017;389:1238–52.
Google Scholar
O’Connor NR, Kumar P. Conservative management of end-stage renal disease without dialysis: a systematic review. J Palliat Med. 2012;15:228–35.
Google Scholar
Song MK. Quality of life of patients with advanced chronic kidney disease receiving conservative care without dialysis. Semin Dial. 2016;29:165–9.
Google Scholar
Cupisti A, Brunori G, Di Iorio BR, D’Alessandro C, Pasticci F, Cosola C, et al. Nutritional treatment of advanced CKD: twenty consensus statements. J Nephrol. 2018;31:457–73.
Google Scholar
Goraya N, Wesson DE. Dietary management of chronic kidney disease: protein restriction and beyond. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2012;21:635–40.
Google Scholar
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Fouque D. Nutritional management of chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:1765–76.
Google Scholar
McAlister L, Pugh P, Greenbaum L, Haffner D, Rees L, Anderson C, et al. The dietary management of calcium and phosphate in children with CKD stages 2-5 and on dialysis-clinical practice recommendation from the Pediatric Renal Nutrition Taskforce. Pediatr Nephrol. 2020;35:501–18.
Google Scholar
Fontes BC, Anjos JSD, Black AP, Moreira NX, Mafra D. Effects of Low-Protein Diet on lipid and anthropometric profiles of patients with chronic kidney disease on conservative management. J Bras Nefrol. 2018;40:225–32.
Google Scholar
Ko GJ, Kalantar-Zadeh K. How important is dietary management in chronic kidney disease progression? A role for low protein diets. Korean J Intern Med. 2021;36:795–806.
Google Scholar
Kistler BM, Moore LW, Benner D, Biruete A, Boaz M, Brunori G, et al. The International Society of Renal Nutrition and Metabolism Commentary on the National Kidney Foundation and Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in Chronic Kidney Disease. J Ren Nutr. 2021;31:116–20.
Google Scholar
Hinkelbein J, Komorowski M, Grau S. Effects of Spaceflight on Astronaut Brain Structure. N Engl J Med. 2018;378:581–3.
Google Scholar
Tovar-Palacio C, Tovar AR, Torres N, Cruz C, Hernandez-Pando R, Salas-Garrido G, et al. Proinflammatory gene expression and renal lipogenesis are modulated by dietary protein content in obese Zucker fa/fa rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2011;300:F263–71.
Google Scholar
Klahr S, Levey AS, Beck GJ, Caggiula AW, Hunsicker L, Kusek JW, et al. The effects of dietary protein restriction and blood-pressure control on the progression of chronic renal disease. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:877–84.
Google Scholar
Mandayam S, Mitch WE. Dietary protein restriction benefits patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrology (Carlton). 2006;11:53–7.
Google Scholar
Jankowski J, Floege J, Fliser D, Bohm M, Marx N. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney disease: pathophysiological insights and therapeutic options. Circulation. 2021;143:1157–72.
Google Scholar
Tonelli M, Wiebe N, Culleton B, House A, Rabbat C, Fok M, et al. Chronic kidney disease and mortality risk: a systematic review. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2006;17:2034–47.
Google Scholar
Carrero JJ, Johansen KL, Lindholm B, Stenvinkel P, Cuppari L, Avesani CM. Screening for muscle wasting and dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2016;90:53–66.
Google Scholar
Workeneh BT, Mitch WE. Review of muscle wasting associated with chronic kidney disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91:1128S–32S.
Google Scholar
Roumeliotis S, Mallamaci F, Zoccali C. Endothelial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease, from biology to clinical outcomes: a 2020 update. J Clin Med. 2020;9:2359.
Google Scholar
Satoh M. Endothelial dysfunction as an underlying pathophysiological condition of chronic kidney disease. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2012;16:518–21.
Google Scholar
Kovesdy CP, Furth S, Zoccali C. World Kidney Day Steering, Obesity and kidney disease: Hidden consequences of the epidemic. Physiol Int. 2017;104:1–14.
Google Scholar
Chang AR, Grams ME, Ballew SH, Bilo H, Correa A, Evans M, et al. Adiposity and risk of decline in glomerular filtration rate: meta-analysis of individual participant data in a global consortium. BMJ. 2019;364:k5301.
Google Scholar
Herrington WG, Smith M, Bankhead C, Matsushita K, Stevens S, Holt T, et al. Body-mass index and risk of advanced chronic kidney disease: Prospective analyses from a primary care cohort of 1.4 million adults in England. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0173515.
Google Scholar
Mustata S, Groeneveld S, Davidson W, Ford G, Kiland K, Manns B. Effects of exercise training on physical impairment, arterial stiffness and health-related quality of life in patients with chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. Int Urol Nephrol. 2011;43:1133–41.
Google Scholar
Roshanravan B, Robinson-Cohen C, Patel KV, Ayers E, Littman AJ, de Boer IH, et al. Association between physical performance and all-cause mortality in CKD. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2013;24:822–30.
Google Scholar
Cupisti A, D’Alessandro C, Fumagalli G, Vigo V, Meola M, Cianchi C, et al. Nutrition and physical activity in CKD patients. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014;39:107–13.
Google Scholar
Vanden Wyngaert K, Van Craenenbroeck AH, Van Biesen W, Dhondt A, Tanghe A, Van Ginckel A, et al. The effects of aerobic exercise on eGFR, blood pressure and VO2peak in patients with chronic kidney disease stages 3-4: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0203662.
Google Scholar
Wu L, Liu Y, Wu L, Yang J, Jiang T, Li M. Effects of exercise on markers of inflammation and indicators of nutrition in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2022;54:815–26.
Google Scholar
Sheng K, Zhang P, Chen L, Cheng J, Wu C, Chen J. Intradialytic exercise in hemodialysis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Nephrol. 2014;40:478–90.
Google Scholar
Fassett RG, Howden EJ, Isbel NM, Coombes JS. Exercise training in chronic kidney disease patients. Sports Med. 2012;42:473–88.
Google Scholar
Castaneda C, Gordon PL, Uhlin KL, Levey AS, Kehayias JJ, Dwyer JT, et al. Resistance training to counteract the catabolism of a low-protein diet in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. Ann Intern Med. 2001;135:965–76.
Google Scholar
Yang Y. Correlation analysis between sports and antiaging based on medical big data. J Sens. 2022;1:3810676.
Correia JC, Ruas JL. Exercised cytokines promote endurance. Science. 2020;368:470–1.
Google Scholar
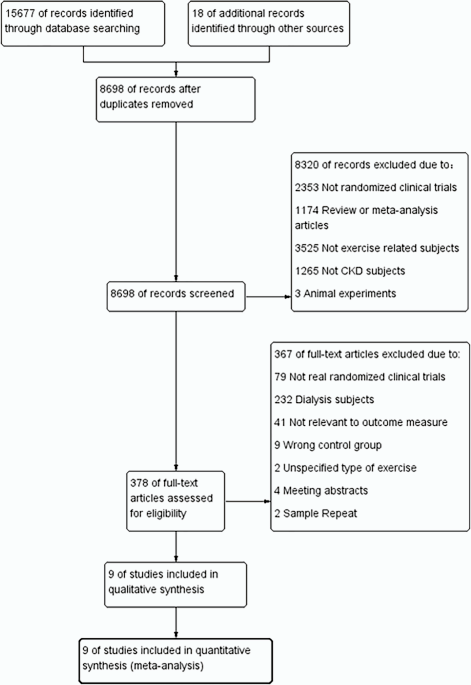
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71.
Google Scholar
Flood L, Constance A. Diabetes and exercise safety. Am J Nurs. 2002;102:47–55.
Google Scholar
Yang YJ. An overview of current physical activity recommendations in primary care. Korean J Fam Med. 2019;40:135–42.
Google Scholar
Shi J, Luo D, Wan X, Liu Y, Liu J, Bian Z, et al. Detecting the skewness of data from the five-number summary and its application in meta-analysis. Stat Methods Med Res. 2023;32:1338–60.
Google Scholar
Luo D, Wan X, Liu J, Tong T. Optimally estimating the sample mean from the sample size, median, mid-range, and/or mid-quartile range. Stat Methods Med Res. 2018;27:1785–805.
Google Scholar
Wan X, Wang W, Liu J, Tong T. Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the sample size, median, range and/or interquartile range. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2014;14:1–13.
Google Scholar
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Juni P, Moher D, Oxman AD, et al. Cochrane Statistical Methods, The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. 2011;343:d5928.
Google Scholar
Aoike DT, Baria F, Kamimura MA, Ammirati A, de Mello MT, Cuppari L. Impact of home-based aerobic exercise on the physical capacity of overweight patients with chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol. 2015;47:359–67.
Google Scholar
Balakrishnan VS, Rao M, Menon V, Gordon PL, Pilichowska M, Castaneda F, et al. Resistance training increases muscle mitochondrial biogenesis in patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:996–1002.
Google Scholar
Baria F, Kamimura MA, Aoike DT, Ammirati A, Rocha ML, de Mello MT, et al. Randomized controlled trial to evaluate the impact of aerobic exercise on visceral fat in overweight chronic kidney disease patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2014;29:857–64.
Google Scholar
Flesher M, Woo P, Chiu A, Charlebois A, Warburton DE, Leslie B. Self-management and biomedical outcomes of a cooking, and exercise program for patients with chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr. 2011;21:188–95.
Google Scholar
Gomes TS, Aoike DT, Baria F, Graciolli FG, Moyses RMA, Cuppari L. Effect of aerobic exercise on markers of bone metabolism of overweight and obese patients with chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr. 2017;27:364–71.
Google Scholar
Gregory SM, Headley SA, Germain M, Flyvbjerg A, Frystyk J, Coughlin MA, et al. Lack of circulating bioactive and immunoreactive IGF-I changes despite improved fitness in chronic kidney disease patients following 48 weeks of physical training. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2011;21:51–6.
Google Scholar
Headley S, Germain M, Milch C, Pescatello L, Coughlin MA, Nindl BC, et al. Exercise training improves HR responses and V O2peak in predialysis kidney patients. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2012;44:2392–9.
Google Scholar
Leehey DJ, Collins E, Kramer HJ, Cooper C, Butler J, McBurney C, et al. Connell, structured exercise in obese diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Nephrol. 2016;44:54–62.
Google Scholar
Naderi N, Kleine CE, Park C, Hsiung JT, Soohoo M, Tantisattamo E, et al. Obesity paradox in advanced kidney disease: from bedside to the bench. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2018;61:168–81.
Google Scholar
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Rhee CM, Chou J, Ahmadi SF, Park J, Chen JL, et al. The obesity paradox in kidney disease: how to reconcile it with obesity management. Kidney Int Rep. 2017;2:271–81.
Google Scholar
Rhee CM, Ahmadi S-F, Kalantar-Zadeh K. The dual roles of obesity in chronic kidney disease. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2016;25:208–16.
Google Scholar
Levin NW, Kotanko P, Eckardt KU, Kasiske BL, Chazot C, Cheung AK, et al. Blood pressure in chronic kidney disease stage 5D-report from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes controversies conference. Kidney Int. 2010;77:273–84.
Google Scholar
Patel SS, Molnar MZ, Tayek JA, Ix JH, Noori N, Benner D, et al. Serum creatinine as a marker of muscle mass in chronic kidney disease: results of a cross-sectional study and review of literature. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2013;4:19–29.
Google Scholar
Rule AD, Larson TS, Bergstralh EJ, Slezak JM, Jacobsen SJ, Cosio FG. Using serum creatinine to estimate glomerular filtration rate: accuracy in good health and in chronic kidney disease. Ann Intern Med. 2004;141:959–61.
Google Scholar
Petreski T, Piko N, Ekart R, Hojs R, Bevc S. Review on inflammation markers in chronic kidney disease. Biomedicines. 2021;9:182.
Google Scholar
Bellizzi V. Low-protein diet or nutritional therapy in chronic kidney disease? Blood Purif. 2013;36:41–6.
Google Scholar
Green DJ, Hopman MTE, Padilla J, Laughlin MH, Thijssen DHJ. Vascular adaptation to exercise in humans: role of hemodynamic stimuli. Physiol Rev. 2017;97:495–528.
Google Scholar
Whyte JJ, Harold Laughlin M. The effects of acute and chronic exercise on the vasculature. Acta Physiol. 2010;199:441–50.
Google Scholar
Oscai LB, Williams BT, Hertig BA. Effect of exercise on blood volume. J Appl Physiol. 1968;24:622–4.
Google Scholar
Schierbauer J, Hoffmeister T, Treff G, Wachsmuth NB, Schmidt WFJ. Effect of exercise-induced reductions in blood volume on cardiac output and oxygen transport capacity. Front Physiol. 2021;12:679232.
Google Scholar
Rodriguez-Iturbe B, Johnson RJ. The role of renal microvascular disease and interstitial inflammation in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2010;33:975–80.
Google Scholar
Luke RG. Hypertensive nephrosclerosis: pathogenesis and prevalence: essential hypertension is an important cause of end-stage renal disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1999;14:2271–8.
Google Scholar
Deus LA, Corrêa HL, Neves RVP, Reis AL, Honorato FS, Araújo TB, et al. Metabolic and hormonal responses to chronic blood-flow restricted resistance training in chronic kidney disease: a randomized trial. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2022;47:183–94.
Google Scholar
Cheema B, Abas H, Smith B, O’Sullivan A, Chan M, Patwardhan A, et al. Progressive exercise for anabolism in kidney disease (PEAK): a randomized, controlled trial of resistalnce training during hemodialysis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2007;18:1594–601.
Google Scholar