Visit news hub
Brain cells communicate with adipose tissue to produce cellular fuel and counteract the effects of aging
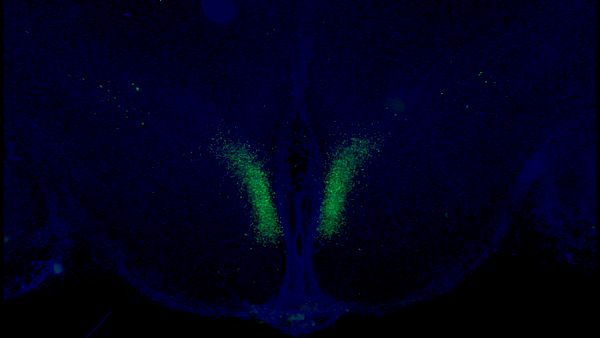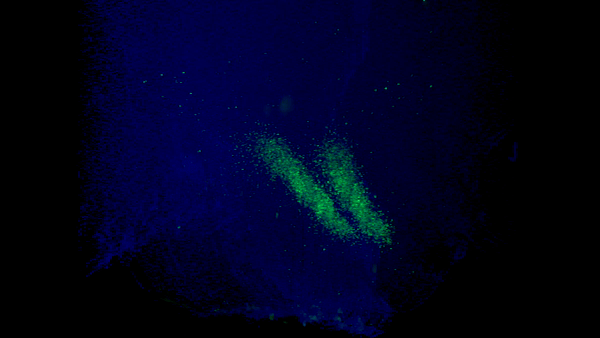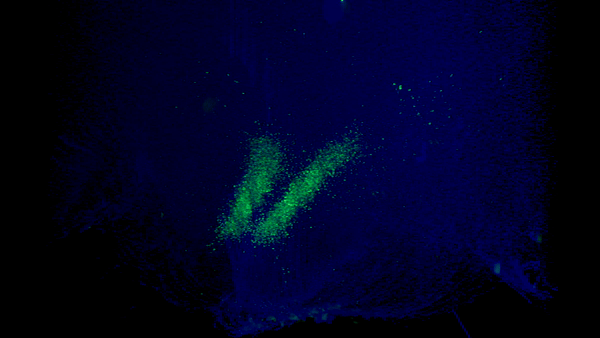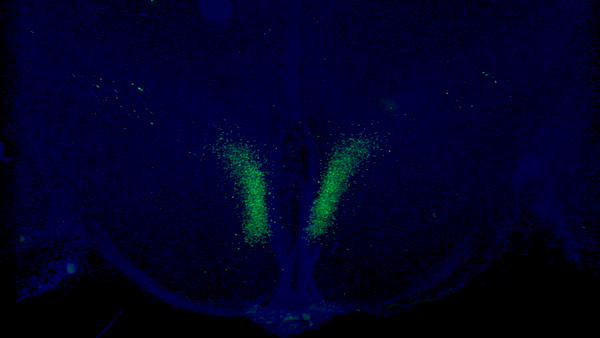
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified a critical feedback loop between the brain and adipose tissue that controls aging in mice. Key neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus of the brain (shown in green) activate adipose tissue to produce cellular fuel. When these specific neurons are activated in older mice, they live longer than control mice.Credit: Kyohei Tokizane
In recent years, research has begun to reveal that the communication pathways between the body’s organs are key regulators of aging. When these lines are open, the body’s organs and systems work better together. However, as we age, our communication lines deteriorate and our organs no longer receive the molecular and electrical messages they need to function properly.
A new study from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has identified in mice a critical communication pathway that connects the brain to the body’s fat tissue in a feedback loop that may be central to energy production throughout the body. This study suggests that the gradual deterioration of this feedback loop contributes to the increase in health problems typical of natural aging.
The study, published Jan. 8 in the journal Cell Metabolism, has implications for the development of future interventions that may maintain feedback loops longer and slow the effects of aging.
Researchers have identified a specific set of neurons in the brain’s hypothalamus that, when activated, send signals to the body’s fatty tissues to release energy. The researchers used genetic and molecular techniques to study mice that were programmed to have this communication pathway open all the time after reaching a certain age. The scientists found that these mice were more physically active, showed signs of delayed aging, and lived longer than mice in which the same communication pathways gradually slowed down as part of normal aging. .
“We demonstrated a way to slow aging and extend healthy lifespans in mice by manipulating key parts of the brain,” said lead author Shinichiro Imai, M.D., Ph.D., professor and Theodore and Bertha Bryan Distinguished Professor of Environmental Medicine. said. He received his PhD from the Department of Developmental Biology at the University of Washington. “Showing this effect in mammals is an important contribution to the field. Previous studies demonstrating lifespan extension in this way have been conducted in less complex organisms such as nematodes and fruit flies. I did.”
These particular neurons, located in a part of the brain called the dorsomedial hypothalamus, produce an important protein, Ppp1r17. When this protein is present in the nucleus, it activates neurons and stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, which controls the body’s fight-or-flight response.
The fight-or-flight response is well known to have far-reaching effects throughout the body, including increasing heart rate and slowing digestion. As part of this response, researchers found that neurons in the hypothalamus trigger a series of events that trigger neurons that innervate white adipose tissue (a type of fat tissue) stored under the skin and in the abdomen. discovered. Activated adipose tissue releases fatty acids into the bloodstream that can be used to promote physical activity. Activated adipose tissue also releases another important protein, an enzyme called eNAMPT, which returns to the hypothalamus and allows the brain to produce fuel for its functions.
This feedback loop is important for providing energy to the body and brain, but it slows down over time. The researchers found that as we age, the protein Ppp1r17 tends to move away from the nucleus of neurons, causing the signals sent by neurons in the hypothalamus to become weaker. With reduced use, the nervous system’s wiring throughout the white adipose tissue gradually recedes, leaving the once dense network of interconnected nerves sparse. Adipose tissue receives fewer signals to release fatty acids and eNAMPT, leading to fat storage, weight gain, and less energy to fuel the brain and other tissues.
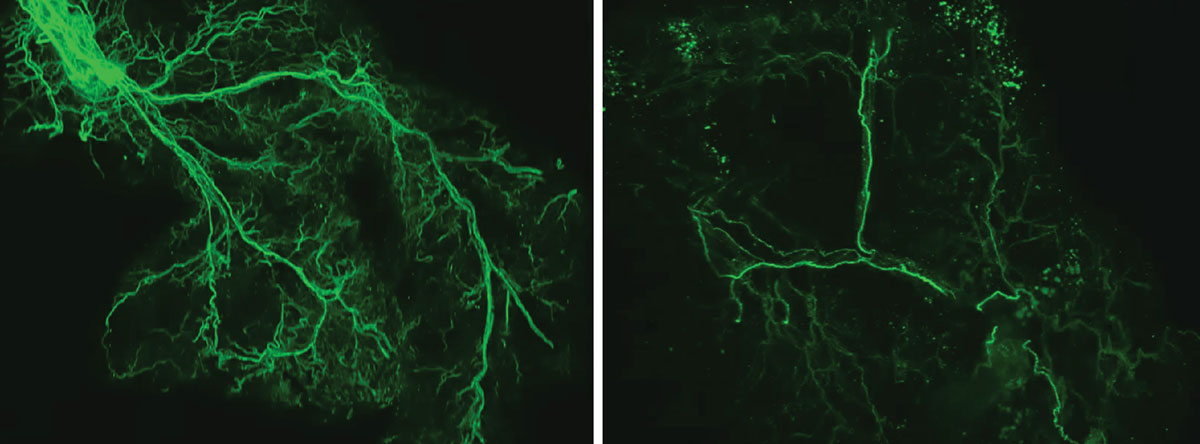
The researchers found that as we age, the protein Ppp1r17 tends to move away from the nucleus of neurons, causing the signals sent by neurons in the hypothalamus to become weaker. With reduced use, the wiring of the nervous system throughout the white adipose tissue gradually recedes, and the once dense network of interconnected nerves (left) becomes sparse (right).Credit: Kyohei Tokizane
Researchers, including lead author Dr. Kyohei Tokizane, a staff scientist and former postdoctoral researcher in the Imai lab, used genetic techniques to induce the retention of Ppp1r17 in neuronal nuclei in the hypothalamus in aged mice. They found that the mice were healthier. They were more physically active, had more running wheels, and lived longer than control mice. They also used a technique that directly activated these specific neurons in the hypothalamus of old mice and observed similar anti-aging effects.
On average, a typical laboratory mouse has an upper lifespan of about 900 to 1,000 days, or about 2.5 years. In this study, all normally aged control mice died by 1,000 days of age. Mice that received an intervention to maintain the brain-adipose tissue feedback loop lived 60 to 70 days longer than control mice. This equates to approximately 7% longer lifespan. For humans, the lifespan of 75 years will increase by about 5 years, if he increases by 7%. The results also suggested that mice that received the intervention were more active at older ages, looked younger, had thicker, shinier coats, and spent more time in a healthier state. .
Imai and his team continue to study ways to maintain the feedback loop between the hypothalamus and adipose tissue. One route they are investigating is supplementing mice with eNAMPT. eNAMPT is an enzyme produced by adipose tissue that returns to the brain to provide energy to tissues such as the hypothalamus. Once released into the bloodstream by adipose tissue, the enzyme is packaged within compartments called extracellular vesicles, where it can be collected and isolated from the blood.
“We can imagine possibilities for anti-aging therapies that include delivering eNAMPT in various ways,” Imai said. “We have already shown that administering eNAMPT into extracellular vesicles increases cellular energy levels in the hypothalamus and extends lifespan in mice. We look forward to continuing our research investigating how to maintain this central feedback loop between the body’s adipose tissues.”