Cell culture conditions
Unless otherwise stated, cells were cultured with DMEM (Sigma Aldrich; #D6429) and 4.5 g/l glucose, phenol red, 10% FBS, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin with pH 7.4 and were incubated at 37 °C, 5% CO2, and 95% relative humidity. Wild-type HepG2 (#300198), HEK293 (#300192), and MCF-7 (#300273) were derived from CLS Cell Lines Service GmbH, HT-29 from Leibniz institute DSMZ (#ACC 299), HepG2 ARE reporter cells from BPS Bioscience (#60513), and HMEpC from Sigma Aldrich (#830-05 A). HMEpC cells were grown in ready-to use human mammary epithelial cell growth medium (Sigma Aldrich; #815-500).
Generation of cell lines
The NRF2 -/- knock-out HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line and Catalase overexpressing HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line were generated by us.
Vectors for CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of 326 bp of human NRF2 gDNA (part of exon 5) are based on vector pSpCas9(BB)−2A-Puro (PX459) V2.0 (Addgene, #62988) and were cloned according to the detailed protocol provided by the Zhang lab41. Top and bottom strand oligonucleotides with 20 bp NRF2-specific guide sequences were annealed and inserted into pSpCas9(BB)−2A-Puro (PX459) V2.0 using scarless cloning with the BbsI restriction enzyme. Oligonucleotides were designed to target sequences followed by NGG at their 3’-end in the genomic context (5’-ACTAAACACAAGTCCCAGTG-3’ and 5’-TTGTGAGATGAGCCTCCAAG-3’, respectively). The resulting vectors were co-transfected into the HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line to obtain the respective reporter with a concomitant NRF2 loss-of-function mutation. Vectors to overexpress human catalase cDNA ORFs are based on vector pcDNA3.1 + /C-HA, containing a neomycin resistance gene and additionally modified to encode a linker followed by a 6xHis tag prior to the C-terminal HA tag. A sequence encoding the human catalase cDNA ORF without stop codon and the last four amino acids was inserted in-frame with the linker6xHis-HA tag encoding sequence, resulting in a vector to overexpress C-terminally tagged human catalase under control of the CMV promoter.
Stable transfection was conducted in 6-well plates with Lipofectamine 3000 Transfection Reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, #L3000008) according to manufacturer’s instructions. Transfected cells were split into 15 cm dish culture plates after 24 h and treatment with selection media started after 48 h. The cells were allowed to grow for 7-14 days and single colonies were picked with the help of cloning discs. Homozygous deletion of NRF2 was confirmed by PCR and catalase overexpression validated via catalase activity assay.
Vectors to overexpress human catalase cDNA ORFs are based on vector pcDNA3.1 + /C-HA, containing a neomycin resistance gene and additionally modified to encode a linker followed by a 6xHis tag prior to the C-terminal HA tag. A sequence encoding the human catalase cDNA ORF without stop codon and the last four amino acids was inserted in-frame with the linker6xHis-HA tag encoding sequence, resulting in a vector to overexpress C-terminally tagged human catalase under control of the CMV promoter.
Stable transgenic cell lines were treated with different antibiotics: HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line with 100 µg/ml hygromycin B, NRF2 -/- knock-out HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line with 100 µg/ml hygromycin B and 0.25 µg/ml puromycin, HepG2 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line with 600 µg/ml G418, and Catalase overexpressing HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cell line with 100 µg/ml hygromycin B and 200 µg/ml G418.
Compound library
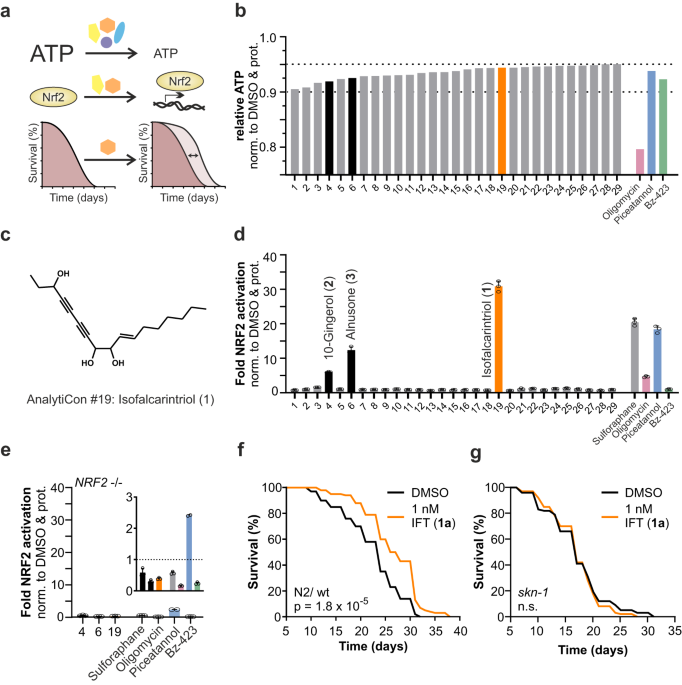
The compound library (MEGx library) was purchased from AnalytiCon Discovery GmbH, Potsdam, Germany. Validation experiments were performed with synthesized isofalcarintriol (1a), 10-gingerol (2) (Sigma Aldrich; #G5798) and alnusone (3) (ChemFaces; #CFN89536).
Bacteria preparation
Unless otherwise stated, C. elegans was cultured at 20 °C on nematode growth media (NGM) seeded with E. coli OP50. Bacteria to feed C. elegans were prepared as previously described42. Briefly, bacteria were cultured overnight at 37 °C with constant shaking in flasks with appropriate media (OP50 in DYT medium, and E. coli HT115 (DE3) in LB medium containing 100 μg mL−1 Ampicillin). Overnight cultures were concentrated by centrifugation for 30 min at 3,200 x g and 4 °C. Concentrated bacteria prepared were spotted on NGM plates and left overnight before use.
Heat inactivated (HIT) OP50 were prepared as previously described43. In short, the overnight OP50 culture was pelleted by centrifugation as above, all DYT media removed, and bacteria resuspended in S-buffer supplemented with 1 M MgSO4 and 5 mg/ml Cholesterol to have a 10-fold concentrated culture. Afterwards, the bacterial suspension was placed in a 65 °C water bath for 45 min. HIT OP50 were spotted on NGM agar plates on the day of use and dried for 30 min before adding the worms.
C. elegans culture & lifespan
Strains that were obtained from Caenorhabditis Genetics Center (University of Minnesota, USA) included Bristol N2 (wild type), EU31 skn-1 (zu135), RB754 aak-2 (ok524), GMC101 (dvls100). AM23 (rmIs298[pF25B3.3::Q19::CFP]) and AM716 (rmIs284[pF25B3.3::Q67::YFP]) strains were kindly provided by R. I. Morimoto. MIR257 risIs28[hsp-16.2p::CTL1::GFP + unc119(+)] was generated by G.G., and has not been published yet. F27C1.7 (atp-3) RNAi was derived from the ORF library v1.1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and H28O16.1 (atp-1) RNAi from the AHR library (Source BioScience, Nottingham, United Kingdom).
The compound or DMSO (solvent control) was added into liquid hot NGM (50 °C) prior to plate pouring. All compound life spans were performed on heat-inactivated OP50. RNAi-mediated gene knockdown experiments, using E. coli HT115 bacteria feeding, was conducted as previously described44. Life span assays with C. elegans were performed as previously described, explicitly by omitting FUdR42, summarized as follows: Adult nematodes were allowed to lay eggs for four to nine hours and the resulting eggs incubated for 64 h at 20 °C on NGM agar plates inoculated with OP50 to obtain a synchronized population of young adult nematodes. For a typical lifespan assay, 100 young adult nematodes per condition were manually transferred to NGM agar plates (30–35 nematodes per 55 mm petri dish) that were inoculated with the respective bacteria as indicated. For the first 10-12 days, nematodes were transferred daily and afterwards every 2-3 days. Nematodes showing no reaction to gentle stimulation were scored as dead. Nematodes that crawled off the plates, displayed internal hatching, or a protruding vulva were censored.
Statistics for lifespan assay are listed in Supplementary Tables 2 and 5.
ATP Assay
HepG2 cells were seeded into a white clear bottom 96– well plates (Greiner Bio-One, #655098) at 24 h prior treatment. Treatment was performed in at least triplicates by the addition of the 5 µg/ml (initial screening) or 10 µM (validation experiments) of compound, or 10 µM of positive controls including oligomycin (Apollo; #APOBIO1002), piceatannol (Sigma Aldrich; #P0453), and Bz-423 (Sigma Aldrich; #SML1944). In case of C. elegans samples, 4M G-HCl was added to previously prepared worm powder, boiled for 15 min and subsequently added to a white clear bottom 96 well plate (Greiner Bio-One, #655098) as 4-fold determination. CellTiter-Glo® Luminescent Cell Viability Assay (Promega; #G7571) was conducted according to manufacturers’ instruction. In addition, an ATP standard row was processed in parallel, and the sample protein quantified via Pierce BCA protein assay (ThermoFisher Scientific). The chemiluminescence of ATP standard plates and cell plates was measured with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH).
NRF2 activation
Approximately 50,000 NRF2 Luciferase Reporter cells were seeded into a white clear bottom 96- well plate (Greiner Bio-One, #655098) and incubated overnight. Parallel to this, another 96 well plate was seeded and treated equally for later protein determination via SRB. After 18-22 h, cells were treated with 5 µg/ml (initial screening) or 10 µM (validation experiments) of compound, 10 µM ATP inhibitors oligomycin, piceatannol and Bz-423, or 5 µM positive control (sulforaphane; Sigma Aldrich; #S4441), respectively. The protein plate was taken for SRB assay analysis, while the NRF2 activity assay plate was prepared for read-out according to manufacturers’ instructions (ONE-GloTM Luciferase Assay System; #E6120) with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH).
Proliferation Assay / SRB Assay
Cells were seeded into a 96 well plate and treated with isofalcarintriol (1a) the day after. Ice-cold TCA (10%) was used for protein precipitation at desired experimental endpoint. Proteins were stained with 0.4% Sulforhodamine B (SRB) (Santa Cruz; #sc-253615A) in 1% acetic acid, washed, and dissolved in Tris. Absorbance was measured at 510 nm with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH).
Cell staining by using click chemistry
HepG2 cells were seeded onto sterile coverslips in 6 well plates with a density of 24,000 cells per well and incubated for 1–2 days. The cells were then treated with 10 µM isofalcarintriol-alkyne (structure S25) overnight. A final concentration of 250 nM MitoTracker deep red (Thermo Fisher Scientific; #M22426) diluted in media was added and plates incubated 30 min at 37 °C/5% CO2. The cells were fixed with 4% PFA and permeabilized with X. Azide-488 (Click Chemistry Tools #1275-1) in click chemistry buffer was added and incubated for 30 min at 37 °C. The coverslips were then positioned upside down in a drop of DAPI-containing mounting media (Thermo Fisher Scientific; #36966/2 ml) on top of a glass dish. Microscopy pictures were taken with an Olympus FluoView 3000 confocal microscope and analyzed with the software Fiji.
Mitochondrial membrane potential
HepG2 cells were seeded in a black clear bottom 96- well plate (Greiner Bio-One, #655090). After overnight incubation, the cells were treated with 10 µM compound, solvent control, or FCCP (Cayman; CAY15218-10mg). After that, the cells were stained with 500 nM tetramethylrhodamine (TMRE) (Sigma Aldrich; #87917). Fluorescence was measured at Ex/Em: 540/595 nm with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH). Raw data were normalized to TMRE-free cells. Afterwards, protein was quantified by Pierce BCA protein assay (ThermoFisher Scientific).
Soft agar colony formation assay
This assay was conducted as described previously45. In short, 5% (w/v) agar stock solution was prepared in PBS, autoclaved and equilibrated at 50 °C. A 0.5% agar solution was prepared and added as bottom layer to 12 well plates. The cells were detached off the cell culture plate by trypsin and 500-2,000 cells per ml were mixed with compound and liquid agar (final concentration of 0.3%). The mixture was added on top of the bottom layer of agar and allowed to solidify for 30 min at RT. Cell culture media was added on top of each well. The plates were incubated 2-3 weeks and the media was changed every 3-4 days. After that, the colonies were stained with 0.01% crystal violet (Sigma Aldrich; #V5265-500ML) and analyzed with a Leica M165FC microscope with Leica camera DFC 3000 G. The number and size of colonies was calculated with ImageJ and the Plugin ColonyCounter.
Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Assay and Real-Time ATP Rate Assay
The Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Assay protocol with C. elegans was adapted from previous publication46. Specifically, synchronized and treated nematodes were diluted in M9 buffer + 25 µM tetramisole hydrochloride (Sigma Aldrich; #L9756) and distributed in a Seahorse XF24 culture plate (Agilent; #102340-100) with approx. 40 worms per well. The cartridge plate was loaded with FCCP (Cayman; CAY15218) and 4 mM NaN3 and calibrated at 20 °C. The measurement was performed with an Agilent Seahorse XF24 Analyzer.
For cells, 100 µl HepG2 were seeded with a density of 30,000 cells per 96 well into a Seahorse XF 96 cell culture plate (Agilent; #102416-100). After an overnight incubation, cells were pre-treated with 10 µM of the compound of interest, solvent control, positive control (10 µM piceatannol, 10 µM Bz-423, 5 µM oligomycin) or untreated culture media. The assay protocols were conducted according to manufactures protocol (Agilent) by using Seahorse XFe96 Flux Pak (Agilent; #102416-100). In short, a Seahorse XF96 cartridge plate (Agilent; #102416-100) was calibrated with 200 µl calibration buffer per well and was incubated in a CO2 free incubator at 37 °C overnight. On the day of experiment, the cell culture growth media was removed and cells were washed twice with 150 µl XF DMEM assay medium, pH 7.4 (Agilent; #103680-100) supplemented with 5 mM glucose, 1 mM pyruvate, and 2 mM glutamine., In a last washing step, 150 µl XF DMEM assay medium with (pre-treatment group) or without (injection group) the compound of interest or solvent control was added. In case of the Cell Mito Stress assay, port A was loaded with compound (for injection samples) or with Seahorse medium (for pre-treated cells), port B with oligomycin (Apollo; APOBIO1002), port C with FCCP (Cayman; CAY15218), and port D with a mixture of antimycin A (Sigma Aldrich; A8674-25MG) and rotenone (Sigma Aldrich; #R8875). In case of the Real-Time ATP Rate assay, the injection of FCCP was skipped. The cartridge plate was inserted into the Agilent Seahorse XF96 Analyzer for calibration at 37 °C. After calibration, the cell plate was inserted and the measurement started. After the run, the media was removed and the cell plate incubated with 10 µl NaOH for 1 h at RT for cell lysis and later the protein was quantification quantified via BCA (Pierce BCA protein assay, ThermoFisher Scientific). Raw data were then normalized to µg of protein and analyzed by Agilent Seahorse Analytics.
ROS quantification by DCF-DA and Amplex Red
25,000 HepG2 cells were seeded in a black clear bottom 96 well plate (Greiner Bio-One, #655090) and incubated overnight. 25 µM DCF-DA (Sigma Aldrich; #D6883) in phenol-free and FBS-free DMEM was added for 45 min at 37 °C. The cells were treated with 10 µM isofalcarintriol (1a), or 1 µM rotenone (Sigma Aldrich; #R8875) for 15 min at 37 °C. Fluorescence was measured at Ex/Em: 485/535 nm with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH). Raw data were normalized to cell-free wells and DCF-DA-free cells. ROS in C. elegans was measured via Amplex Red Assay as previously published47. In short, synchronized worms were treated with 100 μM Amplex Red (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA) and 0.2U/ml of horseradish peroxidase in sodium-phosphate buffer for 3 h. Fluorescence was measured at Ex/Em: 544/590 nm with a CLARIOstar microplate reader (BMG LABTECH). For protein normalization, a Pierce BCA protein assay (ThermoFisher Scientific) was conducted.
Paraquat stress assay
Synchronized L4 stage worms were transferred to isofalcarintriol-containing NGM plates. On day 3 of adulthood, the nematodes were additionally treated with 10 mM paraquat (Sigma Aldrich; #56177). Dead worms were counted in 10-14 h steps and analyzed with JMP.
Thrashing assay /Huntington assay
Synchronized L4 nematodes were were treated with isofalcarintriol (1a) for 5 days at 20 °C. On day 5 of adulthood 10–20 worms were transferred into that liquid drop and their bending movement was recorded for 30 s with a Leica system (Leica M165FC microscope with Leica camera DFC 3000 G). At least 220 nematodes per condition were analyzed during two independent experiments via automatized analysis using the ImageJ plugin “wrMTrck48”. The nematode strains AM23 and AM716 display healthy (AM23) or pathological expression (AM716) of poly Q repeats in the huntingtin gene. Synchronized L4 stage nematodes were put on 25 °C to induce protein expression and were treated with isofalcarintriol (1a) (1 nM) for 48 h. At least 250 nematodes per condition were analyzed during two independent thrashing experiments.
Alzheimer´s assay (GMC 101)
The genetically modified strain GMC 101 (dvIs100 [unc-54p::A-beta-1-42::unc-54 3’-UTR + mtl-2p::GFP]) expresses the human amyloid β peptide. Synchronized L4 nematodes were put on isofalcarintriol (1a) (1 nM) for 24 h. On day 2 of adulthood, they were upshifted to 25 °C to induce protein accumulation. The number of worms with body paralysis was counted every 12 h. For statistics see Supplementary Table 8.
Real-time PCR
Total DNA for mtDNA quantification was extracted from cells or grinded nematodes by standard proteinase K and phenol–chloroform extraction. mtDNA/nDNA levels were quantified in at least three biological replicates using SYBR Green select master mix (Applied Biosystems) fluorescence on a 96-well format in CFX96 real time system (Biorad). mtDNA/nDNA ratios were calculated by 2 × 2 dCT method49. Used primers are based on previous publications49,50,51 and sequences are provided in Supplementary Table 10.
Immunoblotting
Cells were lysed in standard protein isolation buffer and discrupted by sonication. Protein was collected by centrifugation and the concentration determined by Pierce BCA protein assay (ThermoFisher Scientific). C. elegans samples were processes by grinding before SDS-PAGE separation and protein immunoblotting. Antibodies against phospho-AMPKα (Thr172) (40H9) (Cell signaling; #2535, lot 21) were used in a dilution of 1:1000, AMPKα (Cell signaling; #2532, lot 19) in a dilution of 1:1000 and actin (Sigma Aldrich; #A5060) was used in a dilution of 1:3000. The HRP linked secondary antibody against rabbit (Cell Signaling, #7074 S, lot 30) was used at recommended dilutions. The signal was visualized using Clarity Western ECL Substrate (Biorad).
Catalase activity assay
To validate the overexpression of human catalase in HEK293 ARE/NRF2 luciferase reporter cells, cells were lysed, sonicated and centrifuged at 12,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C. The protein supernatant was used for both, protein determination and catalase activity, as described previously52,53 with minor adaptations54.
Biotin Pulldowns and Mass Spectrometry (MS)
For HEK298, 80% confluent cells were harvested by scraping and pelleted by centrifugation (500 x g for 5 min at 4 °C). The cell pellet was dissolved in 250 µl lysis buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.3, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% NP40, 2 mM NaF, 2 mM Na3VO4) and incubated for 15 min on ice. Samples were disrupted by sonication (3x for 2 s; 50% amplitude). Samples were left on ice for 15 min and afterwards centrifuged at 13,000 x g for 5 min at 4 °C. The protein supernatant was collected and quantified by BCA (Pierce BCA protein assay, ThermoFisher Scientific). 2 µl of a 2 mM stock of biotin-alkene (S12) (negative control) was added to 80 µl Dynabeads™ M-280 Streptavidin (ThermoFisher, #11205D) in lysis buffer and incubated in an end-over-end rotator for 30 min at RT. The lysis buffer was removed from the beads and 500 µg of protein per condition was added to the beads and incubated for 4 h at 4 °C on an end-over-end rotator. Meanwhile, new beads were prepared by including both, S12 (negative control) and biotin-isofalcarintriol (3 S,8 R,9 R)-15 (2 µl of a 2 mM stock concentration per condition). When 4 h have passed, the samples were put on the magnetic holder and the supernatant collected in a new tube. The freshly prepared bead-compound mix was mixed with the protein supernatant and incubated another 4 h at 4 °C on an end-over-end rotator. After this incubation time, the beads were washed 5 times with lysis buffer without protease inhibitor and without detergent. Dry beads were frozen in liquid nitrogen until further processed.
For HepG2, 3.5 million cells per 10 cm culture dish were seeded and incubated until reaching 80% confluency. Cells HepG2 cells were then treated with 10 µM biotin-isofalcarintriol (3 S,8 R,9 R)-15 or negative control (biotin-alkene (S12)) for 20 min. Cells were harvested by scraping and pelleted by centrifugation (500 x g for 5 min at 4 °C). The supernatant was removed and the cell pellet was flash-frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80 °C until further needed. Prior to the pull-down assay, the cell pellet was thawed on ice, and dissolved in lysis buffer (20 mM HEPES pH 7.3, 50 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.01% NP40, 2 mM NaF, 2 mM Na3VO4) in a ratio of 4:1 (vol:wt). Afterwards, the samples were disrupted by one freeze and thaw cycle. To degrade nucleic acids, the samples incubated with 0.1% benzonase (250 U/µl) (Sigma Aldrich #E1014-5KU) for 30 min on an end-over-end rotator at 4 °C. After this incubation time, the tubes were centrifuged for 20 min at 16,100 x g at 4 °C and the protein was quantified by BCA and (Pierce BCA protein assay, ThermoFisher Scientific). After determination of the protein concentration, 500 µg of protein per condition was taken and mixed with 40 µl of the Streptavidin beads in lysis buffer by gentle snipping. The samples were incubated on an end-over-end rotator for 4 h at 4 °C to allow binding to the beads. Beads were washed 5 times with lysis buffer without protease inhibitor and detergent. Dry beads were frozen in liquid nitrogen until further processed.
As previously described43, proteins on beads were eluted and digested by adding 20 μl 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) supplemented with 2 M urea, 5 mM DTT and 100 ng Sequencing Grade Trypsin (Promega, #V5111) and incubated for 15 min. Digested protein were reduced by adding more DTT to a final concentration of 10 mM, and alkylated with 3 mM iodoacetamide. The digestion was continued at 32 °C for 6 hours or overnight. pH was checked to ensure that they were within the pH range of 7-9 as it is critical for the optimal trypsinization. All incubation steps were carried out on thermoshaker with gentle shaking at 400 rpm.
The trypsinization was stopped by adding 5% trifluoroacetic acid in several steps until it reached 0.5% TFA, the pH was monitored to ensure it was around. Tryptic peptides were centrifuged at max speed before desalting with self-packed C18 Stage-Tips55. Desalted tryptic peptides were vacuum dried and resolubilized in 20 μl 3% acetonitrile, 0.1% formic acid, with the help of 10 min on thermoshaker and sonication each. Samples from three biological replicates were pooled and Four microliters of digested peptides were injected for shotgun liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) as described below.
All MS experiments were done at the Functional Genomics Center Zurich (FGCZ). As previously described43, peptide mixtures were separated by reversed phase chromatography using Acquity UPLC M-Class system (Waters Inc.) on HSS C18 T3 Col 100 A column (1.8 µm, 75 µm x 250 mm, Waters Inc.). Peptides were separated on a multistep acetonitrile gradient (5–35% in 135 min, 40% in 5 min, and 80% in 1 min) with 0.1% formic acid at a nanoflow rate of 300 nl/min. Eluting peptides were directly ionized by electrospray ionization Orbitrap Fusion Lumos mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific) equipped with a Digital PicoView nanospray source (New Objective) in a data-dependent mode.
All raw data were further analyzed with MaxQuant software suite version 1.6.3.3 (Max Planck Institute of Biochemistry, Munich) supported by the Andromeda search engine56. Data were searched against a UniProt Human proteime database encompassing 75,004 protein entries, downloaded from UniProt (Proteome ID: UP000005640.
Peptides were searched with carbamidomethylation as a fixed modification and protein N-terminal acetylation and methionine oxidation as variable modifications. A maximum of two or four missed cleavages were allowed while requiring strict trypsin specificity, and only peptides with a minimum sequence length of six were considered for further data analysis. Data were search with concatenated target/decoy (forward and reversed) version of the libraries. Only proteins identified with at least 2 peptides were included for quantification. Proteins with ≥1.5-fold intensity over negative control were considered as the interaction partner.
The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium via the PRIDE57 partner repository (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/) with the dataset identifier PXD037671.
Mouse housing conditions
Mouse experiments were performed according to Art.18 Tierschutzgesetz (TSchG), Art. 141 Tierschutzverordnung (TschV), Art. 30 Tierversuchsverordnung (TVV) (all Switzerland) and were approved by the cantonal veterinary office Zürich, Switzerland. The studies were carried out on male and female C57BL/6NRj mice (Janvier Labs). The animals were housed in a specific pathogen-free environment at 22 °C with a reverse 12 h/12 h light/dark cycle with ad libitum excess to water and food. The animals were either fed with chow diet (young animals: Granovit; #10343700PXL15), aged animals: Ssniff Spezialdiäten GmbH; #S8022-S005) or young animals on high fat diet (Ssniff Spezialdiäten GmbH; #E15744-34; 45 kJ% fat). In case of the latter, 6-week-old mice were put on high-fat diet 6 weeks before the start of compound treatment until their sacrifice. Compound supplementation of young mice started at 13 weeks of age by applying 0.1 mg/kg body weight per day of isofalcarintriol (1a) or solvent control via autoclaved drinking water. Aged mice were treated from 16 months of age onwards using the same dose as the young mice (0.1 mg/kg isofalcarintriol or solvent control) in autoclaved drinking water. The drinking bottles were replaced weekly. All animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation at the end of the respective study, except for the aging study, where mice were inspected 4 times per week for health status, and natural deaths were recorded, while moribund animals were sacrificed by cervical dislocation, and recorded as dead. Criteria for sacrifice included progressive body weight loss, unresponsiveness, persistent abnormalities in breathing, large tumor formation, and strong evidence of discomfort and pain.
Treadmill acclimatization and endurance capacity
The mice were familiarized with the treadmill (Panlab/Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, MA) in 4 single training sessions. In case of lacking motivation to run, the animals were motivated with air puffs. Prior to the experiment, a 5 min warm-up at 8 m/min and 10% incline was performed. The endurance capacity experiment for the high-fat diet cohort (29 weeks of age) was conducted with 5% incline at 12-15 min/min until exhaustion or a maximum of 2 h and 2.5 h for males and females, respectively. The endurance capacity experiment with aged mice (18 months of age) was performed with 10% incline at 12-15 min/min until exhaustion or a maximum of 2.5 h.
Metabolic, body composition and blood parameters
Experiments were performed as described previously58 with some adaptations. In short, fasted blood was sampled via submandibular bleeding and collected in heparin-containing tubes. Blood glucose was determined using a hand‐held glucose meter (Bayer Contour XT Meter). Plasma free fatty acids (FFA), triglycerides (TGs), Cholesterol, and HDL, were analyzed by enzymatic reaction (Cobas Mira; La Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Hematology parameters were measured in a sample of whole blood collected at 29 months of age. The sample was run in a Hemavet machine (Drew Scientific, Miami Lakes FL, USA) according to the manufacturer instructions. Parameters measured included white blood cells, neutrophils, lymphocytes, eosinophils, basophils, platelets, hemoglobin, hematocrit. Cytokines in blood plasma samples were processed with the V-PLEX Proinflammatory Panel 1 Mouse Kit (MSD, Rockville, MD, USA) and analyzed with a Sector Imager Microplate Reader (MSD, Rockville, MD, USA) according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Glucose tolerance tests (GTT) were performed in 4‐h‐fasted mice (15 weeks of age in high-fat diet cohort and 20 months of age in aging cohort), by intraperitoneally injecting a bolus of d‐glucose (1-2 mg g−1). PhenoMaster (TSE Systems, Bad Homburg, Germany) open‐circuit calorimetry system was used to measure oxygen consumption and carbon dioxide production over several days following a 24‐h acclimation period. Analysis was done via CalR, a web-based analysis tool for calorimetry experiments59. Body composition was measured by nuclear magnetic resonance (Echo MRI‐100 Body Composition Analyzer; Echo Medical Systems, Huston, TX, USA) as described previously60.
Frailty Index, Grip strength, and Electrocardiogram (ECG)
The frailty index was determined between 22-33 months of age as previously described20 by analyzing 31 non-invasive parameters of aging and the phenotypical age was calculated via machine learning analysis at http://frailtyclocks.sinclairlab.org/21.
Forelimb grip strength was measured via grip strength test meter (Bioseb in vivo Research Instrument) according to manufacturer’s protocol with some adaptations as reported previously. Three measurements per animal (28 months of age) were averaged and normalized to total body mass61.
ECG was measured with ECGenie Machine (Mouse Specifics, Boston MA, USA) according to manufacturer’s protocol by using EMouse Software (Mouse Specifics, Boston MA, USA) and LabChart software (ADI Instruments, Bella Vista NSW, Australia). In short, the mice (27 months of age) were allowed to acclimatize for up to 10 min on the arms of the apparatus. After that, the recording was started for up to 20 minutes depending on the calmness of the animal and the quality of recording. 3-5 recordings per animal were averaged to get a representative reading.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Portfolio Reporting Summary linked to this article.