Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) plays an important role in many of the body’s most important functions, including producing antibodies to fight infections, regulating blood sugar levels, and promoting the effective functioning of the brain and nervous system. Masu.
Symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency can occur when vitamin B6 levels become dangerously low. Signs of vitamin B6 deficiency may include mood changes, mouth and tongue pain, skin lesions, peripheral neuropathy, anemia, and loss of muscle control.
Vitamin B6 deficiency is common, affecting an estimated 10% of Americans. However, some people may not experience symptoms if the deficiency is minimal. People with severe deficiencies due to malnutrition or diseases that cause malabsorption are more likely to develop symptoms.
Low vitamin B6 levels are associated with several mood changes and mental health symptoms. Examples include confusion, brain fog, irritability, anxiety, and depression.
Research shows that people who take vitamin B6 supplements may have lower levels of anxiety and depression. This may be due to vitamin B6’s effect on the nervous system, which helps regulate stress and tension in the body.
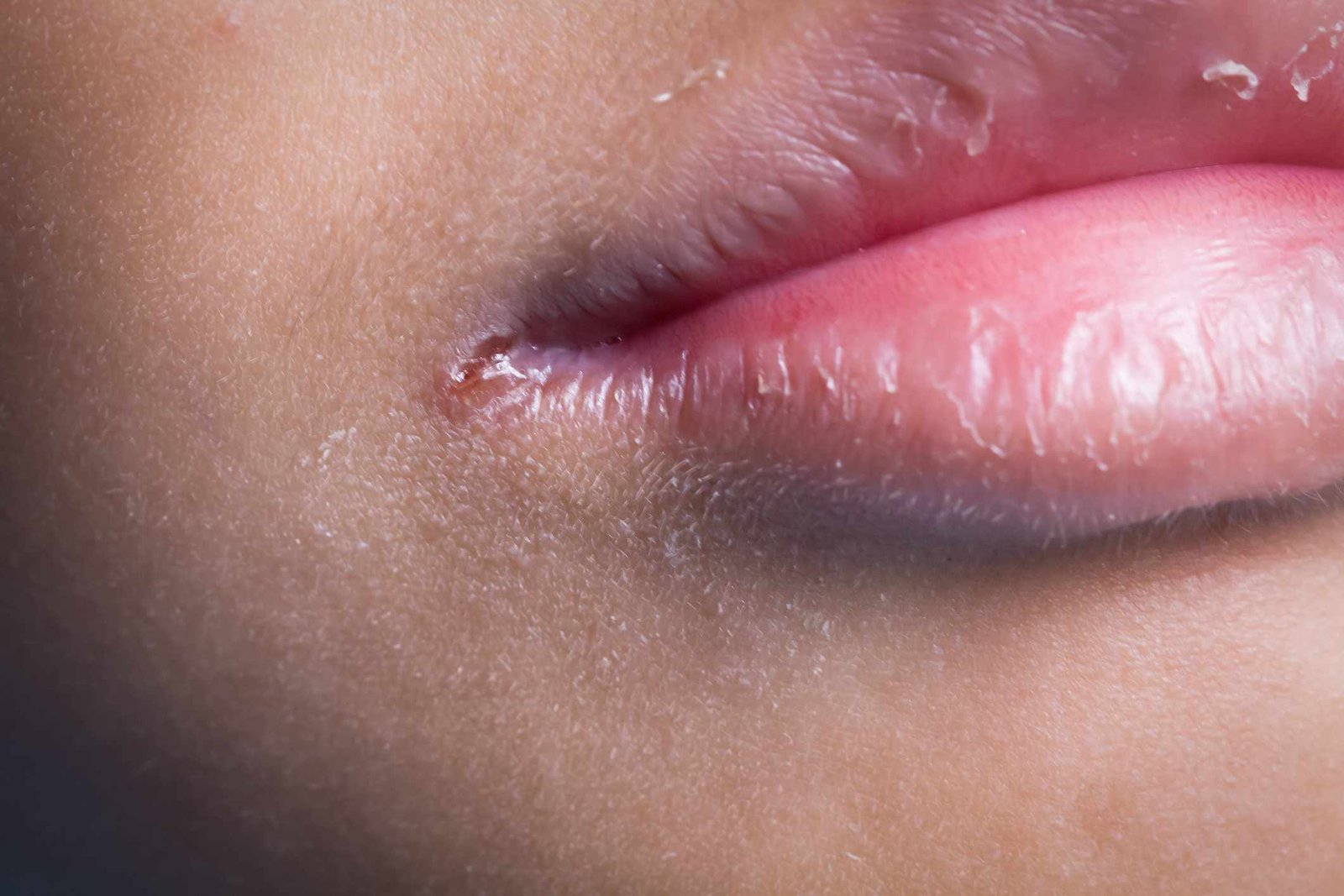
Vitamin B6 deficiency often causes problems with the mouth and tongue. People with extremely low levels of vitamin B6 may develop canker sores, cheilitis (chapped lips), and dryness around the mouth. Some people may experience glossitis (inflammation of the tongue) or tongue pain.
Low vitamin B6 levels can cause a skin disease known as seborrheic dermatitis. Symptoms include a red, scaly, flaky, or greasy skin rash, often affecting the back, face, or scalp. The skin may peel or become inflamed. Researchers believe this is due to inflammation, often caused by vitamin B deficiency.
Vitamin B6 plays an important role in the production of hemoglobin, a protein that helps deliver oxygen to the body’s tissues through the blood. Severe vitamin B6 deficiency can cause a type of anemia known as microcytic anemia, which involves abnormally small red blood cells.
Potential symptoms of anemia include fatigue, shortness of breath, difficulty concentrating, feeling weak, headache, loss of appetite, dizziness, and increased heart rate.
Because vitamin B6 plays a protective role in nerve function, vitamin B6 deficiency can cause nerve damage if left untreated. One possible outcome is peripheral neuropathy, a condition associated with damage to the nerves in the arms, hands, and feet.
People with peripheral neuropathy may experience a tingling or tingling sensation in their extremities, as well as decreased reflexes, numbness, muscle weakness, and pain.
In severe cases, vitamin B6 deficiency can cause ataxia, or loss of muscle control. Signs of ataxia include problems with balance and coordination, clumsiness, difficulty walking, and slurred speech. This is often associated with peripheral neuropathy that affects the extremities.
The signs of vitamin B6 deficiency may be slightly different in infants and young children. Infants who are deficient in vitamin B6 may have the following symptoms:
- irritability and excessive crying
- seizure
- especially sensitive and acute hearing
Contact your health care provider if any of the above symptoms continue to occur. We can perform a physical exam, take a medical history, and test her B6 levels through a serum (blood) test.
Vitamin B6 is found naturally in foods such as legumes (especially chickpeas), beef liver, chicken, and fish. A health care provider may recommend that he get more B6 through dietary changes or supplements, such as pyridoxine supplements alone, B-complex supplements, or multivitamins.
You may be especially at risk for vitamin B6 deficiency if you:
- kidney disease
- liver disease
- Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis
- Digestive disorders that affect the ability to absorb nutrients from food, such as Crohn’s disease
- Alcohol use disorder (AUD)
- obesity
- Other vitamin B deficiencies
If your vitamin B6 deficiency is associated with any of the symptoms listed above, your doctor may recommend treating the underlying disease to resolve your symptoms.
Vitamin B6 deficiency can lead to mental health symptoms such as depression, irritability, and brain fog. It can also cause sores, cracks, and swelling in the mouth and tongue, as well as skin rashes and lesions. Other potential symptoms of vitamin B6 deficiency include anemia, peripheral neuropathy (nerve damage), and ataxia (loss of muscle control). In infants, it can also cause seizures and hearing changes.
If you think you may have a vitamin B6 deficiency, contact your health care provider. We will test your vitamin B6 levels and prescribe supplements if necessary.